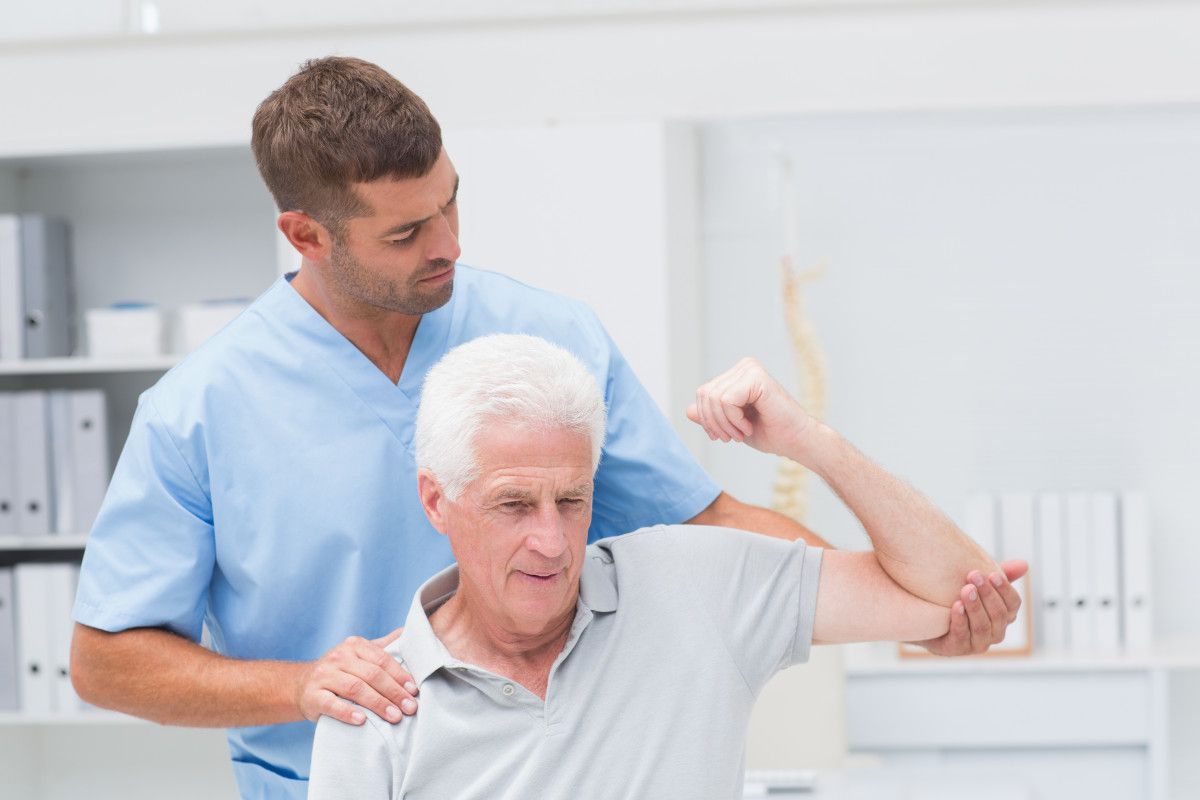
Manual therapy refers to a variety of hands-on techniques used by healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists, chiropractors, osteopaths, and massage therapists, to diagnose, treat, and manage musculoskeletal conditions and pain. It is a non-invasive approach that aims to improve mobility, reduce pain, and restore function in the body.
There are several types of manual therapy techniques, including:
- Massage Therapy: Involves applying pressure, kneading, and manipulating muscles and soft tissues to promote relaxation, reduce tension, and improve circulation.
- Joint Mobilization: A gentle, passive movement of a joint aimed at improving joint mechanics, increasing range of motion, and reducing pain and stiffness.
- Joint Manipulation: Also known as high-velocity low-amplitude (HVLA) thrust, this technique involves a quick and controlled force applied to a joint to improve mobility and reduce joint restrictions.Soft
- Tissue Mobilization: Focuses on the manipulation of soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and ligaments, to relieve pain, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
- Myofascial Release: Targets the fascia, a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, to release tension and improve mobility.
- Trigger Point Therapy: Addresses specific points of muscle tightness and hyperirritability (trigger points) to alleviate pain and improve muscle function.
- Muscle Energy Techniques (MET): Involves active muscle contractions and stretching to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
- Strain-Counterstrain: A gentle technique that positions the body to reduce strain in specific tissues and relieve pain.
- Mulligan Concept: Uses manual techniques and movement to improve joint alignment and function.
- McKenzie Method: A specialized approach to assess and treat spinal and musculoskeletal conditions by using specific exercises and movements.Manual therapy is often used in conjunction with other treatment modalities like therapeutic exercise, stretching, and patient education. It is commonly employed for various conditions, including back pain, neck pain, joint injuries, sports injuries, and other musculoskeletal dysfunctions.It’s essential to note that manual therapy should be performed by trained and licensed healthcare professionals. Before undergoing any manual therapy treatment, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to ensure it is appropriate for your specific condition and medical history.